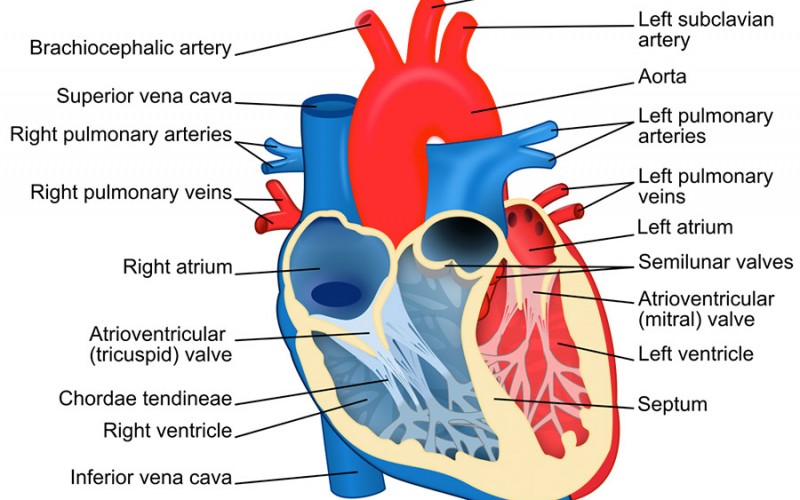
Various heart conditions require an understanding of different parts of the heart. Each part has important functions that contribute to the organ’s normal works.
Chordae tendineae seems like a thin and insignificant part of your heart. However, these thin, string-like tissues are important in keeping a normal blood pumping action throughout the heart.
Chordae tendineae is commonly known as the “heart strings” due to the shape. They connect the heart’s valve with the muscles and consist of 80 percent collagen. They are flexible yet strong despite the seemingly fragile shapes. The heart strings help to keep the overall normal shape of your heart, but they have other function that supports the heart’s work.
Chordae tendineae works like a gate, opening and closing the heart’s valve during the blood circulation. This function allows the heart to pump blood regularly, without causing problems like blood surging or backflow.
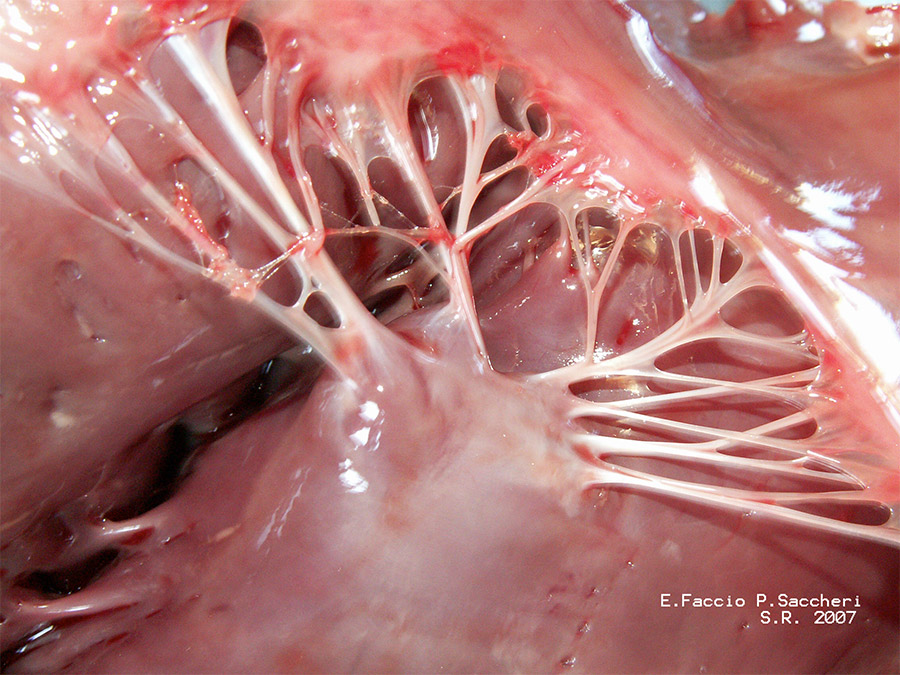
Normal chordae tendineae strings will close the flap tightly during the blood-pumping action, but this is not always the case.
A person may develop Mitral Valve Prolapse, in which the valve is unable to close properly. This condition can be related closely to chordae tendineae and may cause unpleasant symptoms. Learn everything you need to know about mitral valve prolapse here to understand what to expect when you are diagnosed.
Definition of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse is more commonly known as the “click-murmur syndrome”, referring to the murmur (irregular sounds) from your heart due to the unstable blood flow.
This condition often affects the mitral valve flaps, which pump blood to the heart’s left atrium. If a healthy person’s heart pumps blood normally during the heart contraction, mitral valve prolapse prevents this function.
A person with this condition usually has a heart with a bulging valve (or valves). When his or her heart contracts, the valve cannot close properly, resulting in backflow and rush of blood.
A doctor may notice something wrong when he or she sticks a stethoscope on the person’s chest. The sound of the heart will be irregular due to the blood rush.
Mitral valve prolapse is also known as Barlow’s Syndrome. It is thought to affect around three percent of people worldwide. Researchers have still not found the exact cause of this condition. However, people with a family history of mitral valve prolapse may also develop this condition, proving that it is hereditary.
Types of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Despite its effect to the chordae tendineae and the heart’s flaps, these signs are not always present in mitral valve prolapse. It depends on the type of prolapse a person develops. There are two types of mitral valve prolapse, which are:
Primary Mitral Valve Prolapse
Primary mitral valve prolapse is the type that affects the heart flaps and the string muscles.
In this case, the thickening of a flap (or two flaps) plus the abnormalities of chordae tendineae cause the blood to rush more quickly. Primary mitral valve prolapse is common among people with diseases or syndromes affecting their tissues.
Secondary Mitral Valve Prolapse
Secondary mitral valve prolapse doesn’t include the abnormalities on the heart flaps and string muscles.
In this case, the causes are often the other heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease and rheumatic heart disease. These conditions cause a decrease in the blood flow, resulting in pumping action abnormalities.
Some people have mitral valve prolapse without they realize it. Others may experience mild symptoms that not really affect their daily life. However, in a few cases, this condition requires treatments, especially if the symptoms start to annoy and hinder you in real life.
Symptoms of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Not everyone experiences symptoms with this condition, but others have them. Otherwise, you may feel the signs but not immediately get diagnosed.
Here are several common symptoms of Mitral Valve Prolapse.
Irregular Heart Beats
Palpitations, or irregular heartbeats, are the most common symptoms of this condition. These signs usually imply that the patient has abnormal rhythms.
However, palpitations may happen to everyone, even the ones with a supposedly healthy heart. Note that low potassium level can cause palpitations, too.
Chest Pain
Chest pain in Mitral Valve Prolapse is unique; it regularly comes during the most unexpected ways and can be very painful.
Fatigue and Difficulties in Breathing

When the heart flaps and chordae tendineae are weakened, they may affect the whole blood flow.
Your heart may expand and leaked here and there, resulting in inadequate blood flow and even heart failure.
Stroke
Stroke can happen if your heart’s valve leaks and causes blood clotting. This symptom usually only happens in the most severe cases, especially when most of the heart’s parts are damaged.
If these symptoms are starting to become more prevalent, or if they affect your daily life, go to the doctor immediately.
How to Detect Mitral Valve Prolapse
Since doctors cannot directly see your chordae tendineae or heart flaps, mitral valve prolapse can be hard to detect.
Many people find out about their conditions during a routine checkup, where their doctors placing stethoscopes on their chests and discover the murmur sounds. These murmurs come from the backflow of the blood.
Other common sounds are the “clicks”, which come from the abnormally stretched flaps. The flaps snap against each other when your heart contracts because the heart strings are unable to hold them tight. The doctor may hear the murmurs along with the clicks, or just one of them.
If you have a concern about mitral valve prolapse, or if someone in your family history had this condition, you may conduct a checkup. Here are several ways to diagnose mitral valve prolapse:
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram uses the echo of soundwaves to detect the condition of your heart. The soundwaves echo in your heart and create images on the screen.
Any abnormalities on the flaps or chordae tendineae will be apparent through this soundwave scan.
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
EKG is a more common testing method for mitral valve prolapse. However, it gives a more accurate reading if you suffer from a secondary mitral valve prolapse.
The EKG mostly detects things like abnormal heart rhythms and electrical activities.
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac MRI is not the primary diagnosis method for mitral valve prolapse. However, its detailed image results are used to support the echocardiogram result. Cardiac MRI is also used if someone is about to undergo surgery.
Stress Test
Stress Test is basically the EKG, but with the person walks on a treadmill. It is used to monitor the heart’s works when the body is exercising. During this test, the doctor usually conducts other health checkups, such as measuring the blood pressure rate and the ability to breathe.
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is a slightly invasive method since it uses an injection and X-ray scan to detect the heart’s condition. This is a great way to detect the causes of mitral valve prolapse that originate from abnormalities in the organ.
Once mitral valve prolapse is diagnosed, the doctor and patient must discuss to talk whether the treatment is worth the time and cost or not.
How to Treat Mitral Valve Prolapse
In many cases, Mitral Valve Prolapse patient doesn’t need any “treatments”, especially if the symptoms are not annoying you in the real world. You only need to come to the doctor regularly for checkups.
The doctor will check things like your family history, allergy, all the signs you experience, and the severity of the disease.
If resting alone cannot solve the problem, you get several alternatives to discuss with the doctor. They are:
Beta Blockers
Beta Blockers are medication types that return the heartbeats to normal. This is a popular method for people who have irregular heartbeats. You must avoid caffeine sources while consuming these medications.
Anticoagulant
Anticoagulant prevents the forming of blood clots, which is useful if the left part of the heart shows signs of enlargement. Anticoagulant helps you to reduce the risk of having a stroke.
Surgery
The most extreme solution only applies to the worst cases of Mitral Valve Prolapse. This method is recommended if the main cause is abnormalities in the heart muscular system. They can be something like ruptured chordae tendineae, wonky mitral leaflet, or valve lengthening.
If you also experience symptoms like fatigue and dizziness, make sure you drink a lot of water. Add a little salt to the water to make the water level in your heart more balanced.
There’s a minimally invasive mitral valve repair method to help fix your “broken” mitral valve.
Conclusion
Mitral Valve Prolapse happens when your heart’s left flaps cannot contract properly, resulting in blood rush and murmurs.
It may damage the chordae tendineae, but it depends on the prolapse types. You need thorough diagnosis and solutions to detect the prolapse, before getting the right treatments.


Leave a Reply